BMI Calculator
BMI CALCULATOR
BMI CALCULATOR
Welcome to our BMI Calculator!
Our BMI Calculator is a handy tool designed to help you quickly determine your Body Mass Index (BMI). By simply entering your weight and height, you can discover your BMI and gain insight into your overall health. Whether you’re looking to maintain a healthy weight, track your fitness progress, or simply understand your body composition better, our BMI Calculator is here to assist you.
Let’s get started on your journey to better health!
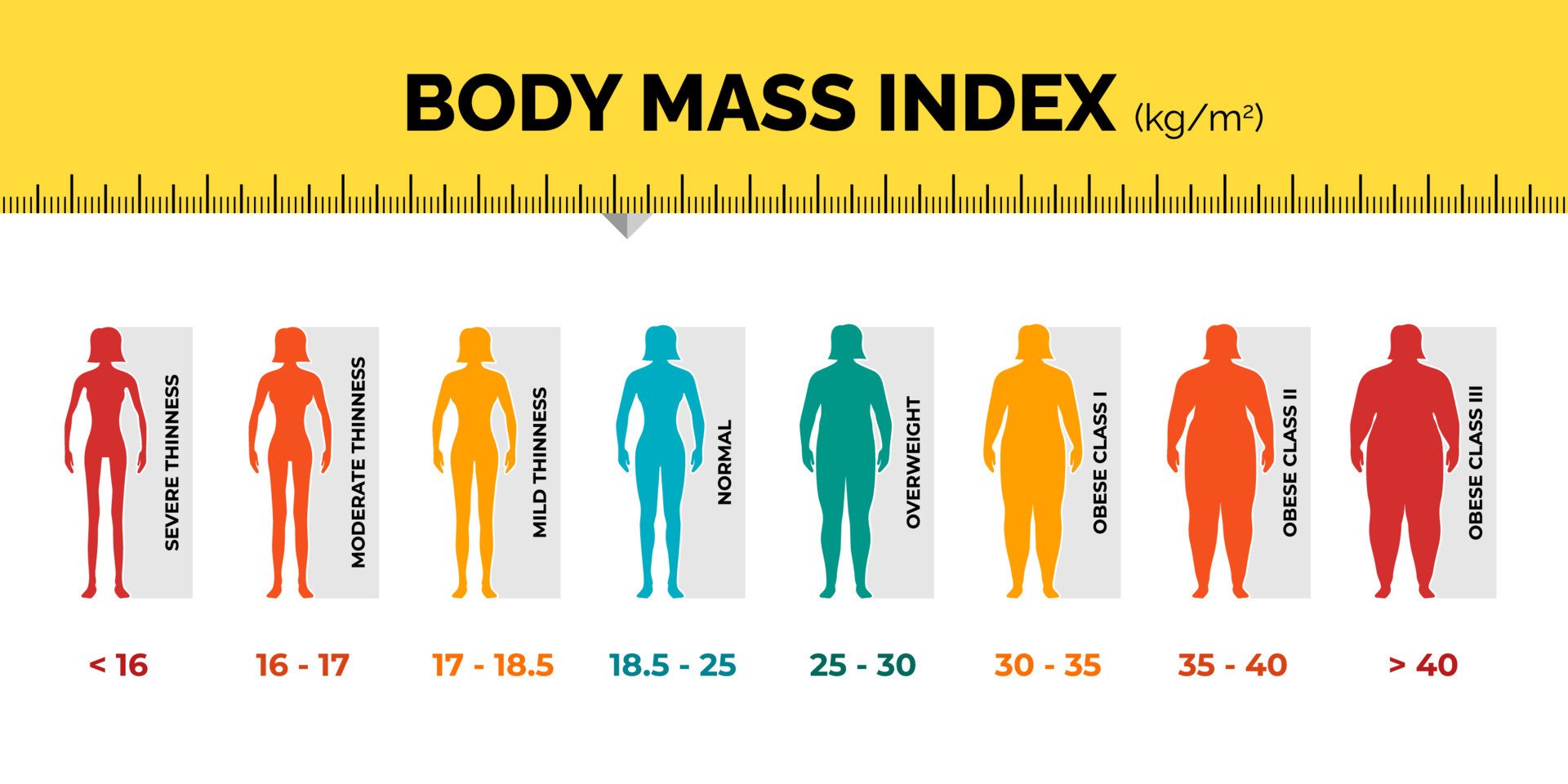
BMI Classification Guide: Understanding Body Mass Index
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure to assess a person’s body weight in relation to their height. It provides a numerical value that categorizes individuals into different weight status groups, ranging from underweight to obese. Understanding BMI classifications is essential for assessing one’s health status and identifying potential risks associated with weight.
1. Severely Underweight (BMI < 16):
- Individuals with a BMI below 16 are categorized as severely underweight.
- This level of underweight can indicate severe malnutrition and significantly increased health risks.
- Medical attention and nutritional intervention may be required to address the underlying causes of severe underweight.
2. Very Underweight (16 ≤ BMI < 16.9):
- BMI falling between 16 and 16.9 indicates very underweight status.
- Individuals in this category may experience significant health risks due to insufficient body weight.
- Adequate nutrition and medical supervision are crucial to improve weight status and overall health.
3. Underweight (17 ≤ BMI < 18.4):
- Individuals with a BMI between 17 and 18.4 are classified as underweight.
- While not as severe as very underweight, being underweight can still pose health risks, such as nutrient deficiencies and weakened immune function.
- Proper nutrition and lifestyle modifications may be recommended to achieve a healthier weight.
4. Normal Weight (18.5 ≤ BMI < 24.9):
- BMI falling within the range of 18.5 to 24.9 indicates a normal weight status.
- Individuals in this category typically have a balanced weight-to-height ratio, which is associated with lower health risks.
- Maintaining a normal weight through healthy eating habits and regular physical activity is essential for overall well-being.
5. Overweight (25 ≤ BMI < 29.9):
- Overweight status is indicated by a BMI between 25 and 29.9.
- Excess weight in this range can increase the risk of various health conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension.
- Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and increased physical activity, are often recommended to manage weight and reduce health risks.
6. Obese Class I (30 ≤ BMI < 34.9):
- Individuals with a BMI between 30 and 34.9 are classified as obese class I.
- Obesity at this level is associated with moderate health risks, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and certain cancers.
- Comprehensive lifestyle interventions, such as dietary counseling, exercise programs, and behavioral therapy, may be necessary for weight management and risk reduction.
7. Obese Class II (35 ≤ BMI < 39.9):
- BMI falling within the range of 35 to 39.9 indicates obese class II status.
- Individuals in this category face severe health risks, including a higher likelihood of developing obesity-related comorbidities like type 2 diabetes and sleep apnea.
- Medical supervision and intensive interventions, such as medically supervised weight loss programs or bariatric surgery, may be recommended for managing obesity and improving health outcomes.
8. Obese Class III (BMI ≥ 40):
- Obese class III, also known as morbid obesity, is characterized by a BMI of 40 or higher.
- This level of obesity is associated with a significantly increased risk of life-threatening health conditions, such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and severe joint problems.
- Multidisciplinary approaches, including medical, nutritional, and psychological support, are often necessary to address the complex health issues associated with morbid obesity and improve overall quality of life.
Share this article

BMI CALCULATOR
BMI CALCULATOR
Welcome to our BMI Calculator!
Our BMI Calculator is a handy tool designed to help you quickly determine your Body Mass Index (BMI). By simply entering your weight and height, you can discover your BMI and gain insight into your overall health. Whether you’re looking to maintain a healthy weight, track your fitness progress, or simply understand your body composition better, our BMI Calculator is here to assist you.
Let’s get started on your journey to better health!
BMI Classification Guide: Understanding Body Mass Index
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure to assess a person’s body weight in relation to their height. It provides a numerical value that categorizes individuals into different weight status groups, ranging from underweight to obese. Understanding BMI classifications is essential for assessing one’s health status and identifying potential risks associated with weight.
1. Severely Underweight (BMI < 16):
- Individuals with a BMI below 16 are categorized as severely underweight.
- This level of underweight can indicate severe malnutrition and significantly increased health risks.
- Medical attention and nutritional intervention may be required to address the underlying causes of severe underweight.
2. Very Underweight (16 ≤ BMI < 16.9):
- BMI falling between 16 and 16.9 indicates very underweight status.
- Individuals in this category may experience significant health risks due to insufficient body weight.
- Adequate nutrition and medical supervision are crucial to improve weight status and overall health.
3. Underweight (17 ≤ BMI < 18.4):
- Individuals with a BMI between 17 and 18.4 are classified as underweight.
- While not as severe as very underweight, being underweight can still pose health risks, such as nutrient deficiencies and weakened immune function.
- Proper nutrition and lifestyle modifications may be recommended to achieve a healthier weight.
4. Normal Weight (18.5 ≤ BMI < 24.9):
- BMI falling within the range of 18.5 to 24.9 indicates a normal weight status.
- Individuals in this category typically have a balanced weight-to-height ratio, which is associated with lower health risks.
- Maintaining a normal weight through healthy eating habits and regular physical activity is essential for overall well-being.
5. Overweight (25 ≤ BMI < 29.9):
- Overweight status is indicated by a BMI between 25 and 29.9.
- Excess weight in this range can increase the risk of various health conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension.
- Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and increased physical activity, are often recommended to manage weight and reduce health risks.
6. Obese Class I (30 ≤ BMI < 34.9):
- Individuals with a BMI between 30 and 34.9 are classified as obese class I.
- Obesity at this level is associated with moderate health risks, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and certain cancers.
- Comprehensive lifestyle interventions, such as dietary counseling, exercise programs, and behavioral therapy, may be necessary for weight management and risk reduction.
7. Obese Class II (35 ≤ BMI < 39.9):
- BMI falling within the range of 35 to 39.9 indicates obese class II status.
- Individuals in this category face severe health risks, including a higher likelihood of developing obesity-related comorbidities like type 2 diabetes and sleep apnea.
- Medical supervision and intensive interventions, such as medically supervised weight loss programs or bariatric surgery, may be recommended for managing obesity and improving health outcomes.
8. Obese Class III (BMI ≥ 40):
- Obese class III, also known as morbid obesity, is characterized by a BMI of 40 or higher.
- This level of obesity is associated with a significantly increased risk of life-threatening health conditions, such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and severe joint problems.
- Multidisciplinary approaches, including medical, nutritional, and psychological support, are often necessary to address the complex health issues associated with morbid obesity and improve overall quality of life.
