Body Mass Index (BMI) 32 Category of Obesity
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a commonly used measure to assess an individual’s body weight relative to their height. It is a useful tool for identifying potential health risks associated with weight status. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore BMI, its calculation, interpretation, associated health risks, and recommendations for maintaining a healthy weight.
BMI Calculator
Understanding BMI:
1. Calculation:
- BMI is calculated using the following formula: ���=Weight in kilograms(Height in meters)2
2. Interpretation:
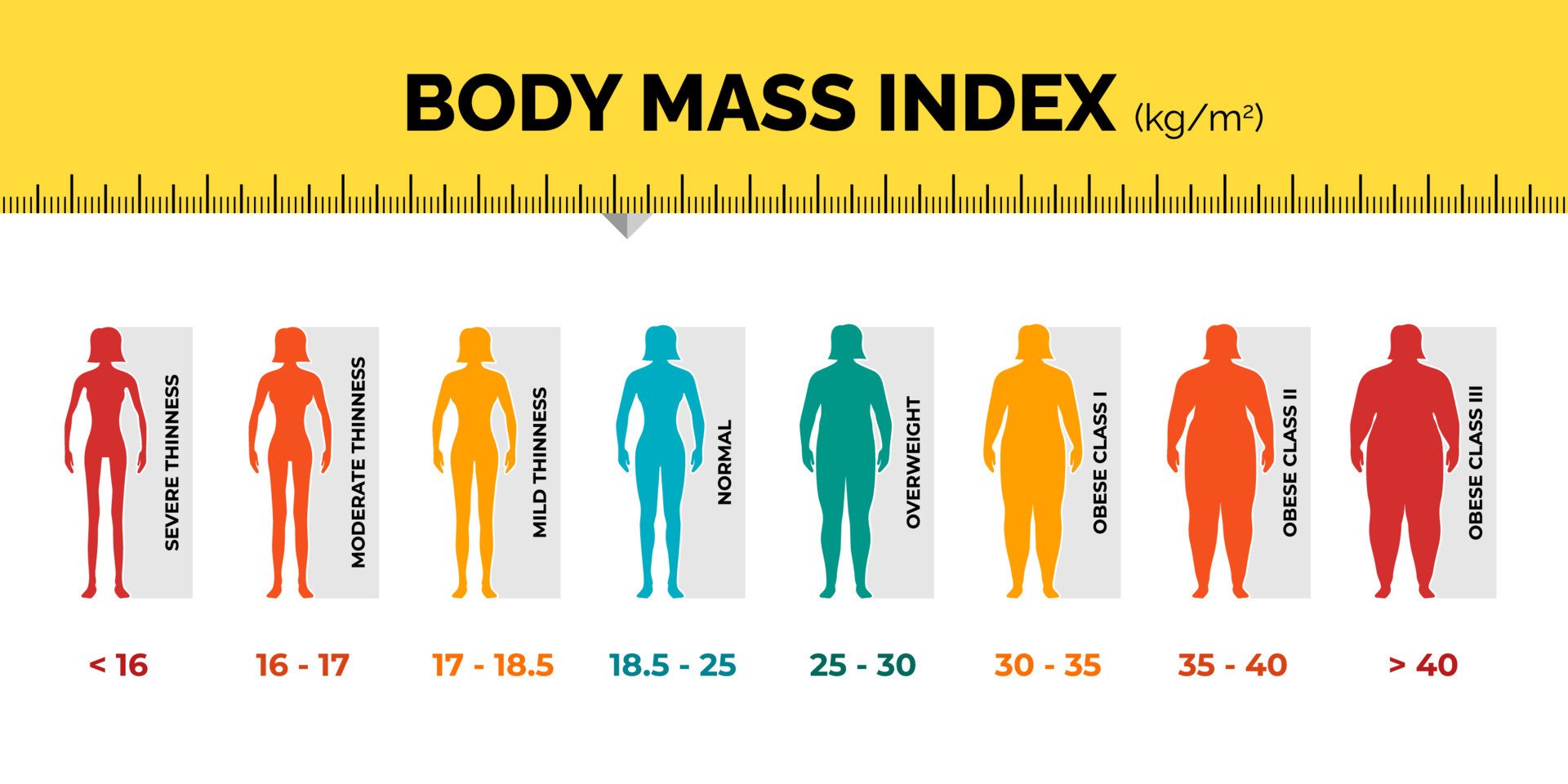
- BMI Categories:
- Underweight: BMI < 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 ≤ BMI < 24.9
- Overweight: 25 ≤ BMI < 29.9
- Obesity: BMI ≥ 30
3. Limitations:
- While BMI is a useful screening tool, it has limitations, including:
- It does not differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass.
- It may not accurately assess body composition in certain populations, such as athletes or older adults.
BMI 32:
A BMI of 32 falls within the “Obesity” category. This indicates an increased risk of various health conditions associated with excess body weight.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity:
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for:
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
- Obesity increases the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Obesity contributes to the development of metabolic syndrome, characterized by a cluster of conditions including hypertension, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and abdominal obesity.
- Obesity is associated with an increased risk of:
5. Joint Problems:
- Excess weight places additional stress on joints, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis and joint pain.
6. Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- Obesity is linked to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gallbladder disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
7. Certain Cancers:
- Obesity is a risk factor for various cancers, including breast, colon, endometrial, and pancreatic cancer.
8. Psychological Impact:
- Obesity can contribute to psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
Recommendations for Managing BMI 32:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise and strength training.
- Limiting the intake of high-calorie, processed foods and sugary beverages.
- Practicing portion control and mindful eating.
2. Behavioral Therapy:
- Seeking support from a registered dietitian or behavioral therapist to address emotional eating, stress management, and behavior modification.
3. Medical Management:
- Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on weight management strategies.
- In some cases, medication may be prescribed to assist with weight loss, particularly for individuals with obesity-related comorbidities.
4. Surgical Intervention:
- Bariatric surgery may be considered for individuals with severe obesity who have not achieved weight loss with lifestyle modifications and medical management.
5. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Monitoring BMI and overall health status regularly.
- Seeking medical attention for any concerning symptoms or changes in health status.
Share this article

Body Mass Index (BMI) is a commonly used measure to assess an individual’s body weight relative to their height. It is a useful tool for identifying potential health risks associated with weight status. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore BMI, its calculation, interpretation, associated health risks, and recommendations for maintaining a healthy weight.
BMI Calculator
Understanding BMI:
1. Calculation:
- BMI is calculated using the following formula: ���=Weight in kilograms(Height in meters)2
2. Interpretation:
- BMI Categories:
- Underweight: BMI < 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 ≤ BMI < 24.9
- Overweight: 25 ≤ BMI < 29.9
- Obesity: BMI ≥ 30
3. Limitations:
- While BMI is a useful screening tool, it has limitations, including:
- It does not differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass.
- It may not accurately assess body composition in certain populations, such as athletes or older adults.
BMI 32:
A BMI of 32 falls within the “Obesity” category. This indicates an increased risk of various health conditions associated with excess body weight.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity:
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for:
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
- Obesity increases the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Obesity contributes to the development of metabolic syndrome, characterized by a cluster of conditions including hypertension, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and abdominal obesity.
- Obesity is associated with an increased risk of:
5. Joint Problems:
- Excess weight places additional stress on joints, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis and joint pain.
6. Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- Obesity is linked to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gallbladder disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
7. Certain Cancers:
- Obesity is a risk factor for various cancers, including breast, colon, endometrial, and pancreatic cancer.
8. Psychological Impact:
- Obesity can contribute to psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
Recommendations for Managing BMI 32:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise and strength training.
- Limiting the intake of high-calorie, processed foods and sugary beverages.
- Practicing portion control and mindful eating.
2. Behavioral Therapy:
- Seeking support from a registered dietitian or behavioral therapist to address emotional eating, stress management, and behavior modification.
3. Medical Management:
- Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on weight management strategies.
- In some cases, medication may be prescribed to assist with weight loss, particularly for individuals with obesity-related comorbidities.
4. Surgical Intervention:
- Bariatric surgery may be considered for individuals with severe obesity who have not achieved weight loss with lifestyle modifications and medical management.
5. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Monitoring BMI and overall health status regularly.
- Seeking medical attention for any concerning symptoms or changes in health status.
