Body Mass Index (BMI) 35 category of obesity
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value calculated based on an individual’s height and weight. It is commonly used as an indicator of body fatness and serves as a screening tool for assessing weight status and associated health risks. A BMI of 35 falls within the category of obesity, which is defined as having excess body fat that can negatively impact health. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore BMI, its calculation, significance, health implications, management strategies, and the importance of maintaining a healthy weight.
BMI Calculator
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI):
1. Calculation:
- BMI is calculated using the following formula: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)^2.
- For example, if an individual weighs 100 kilograms and has a height of 1.75 meters, their BMI would be calculated as follows: BMI = 100 / (1.75^2) = 32.65.
2. Interpretation:
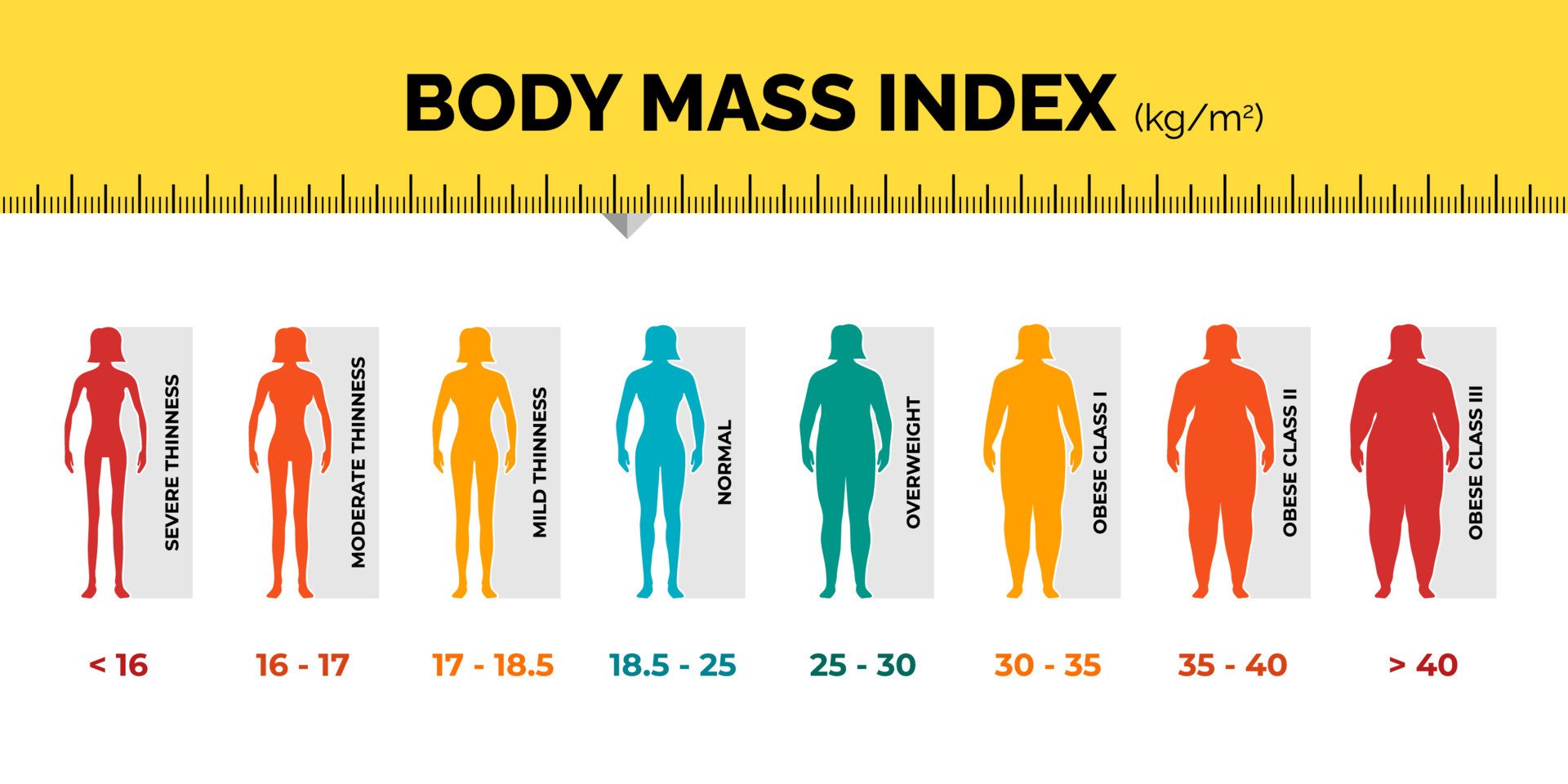
- BMI values are categorized as follows:
- Underweight: BMI < 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5 – 24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25 – 29.9
- Obesity:
- Class I (Moderate): BMI 30 – 34.9
- Class II (Severe): BMI 35 – 39.9
- Class III (Very Severe or Morbid): BMI ≥ 40
Health Implications of BMI 35:
1. Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases:
- Obesity, particularly at BMI 35 or higher, is associated with an increased risk of various chronic diseases, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Disease (e.g., heart disease, stroke)
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- Dyslipidemia (Abnormal Cholesterol Levels)
- Certain Cancers (e.g., breast, colorectal)
- Sleep Apnea
- Osteoarthritis
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
2. Impact on Quality of Life:
- Obesity can significantly impair physical function and mobility, leading to decreased quality of life and increased disability.
- Individuals with obesity may experience limitations in activities of daily living and face challenges in social and professional settings.
3. Psychological and Emotional Effects:
- Obesity can have psychological and emotional repercussions, including:
- Low self-esteem
- Depression and anxiety
- Body image dissatisfaction
- Social stigma and discrimination
Management Strategies for BMI 35:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet low in calorie-dense foods and high in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise to promote weight loss, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
- Behavioral Strategies: Implementing behavioral changes such as mindful eating, portion control, and stress management techniques to support long-term weight management.
2. Medical Interventions:
- Pharmacotherapy: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to assist with weight loss. These medications may include appetite suppressants, lipase inhibitors, or medications that alter satiety and energy expenditure.
- Bariatric Surgery: For individuals with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 40 or BMI ≥ 35 with obesity-related comorbidities), bariatric surgery may be recommended as a treatment option. Procedures such as gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding can result in significant and sustained weight loss, along with improvements in obesity-related health conditions.
3. Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Obesity management often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties, including physicians, dietitians, psychologists, and exercise physiologists. Collaborative care allows for comprehensive assessment, individualized treatment planning, and ongoing support for behavior change.
Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
1. Reduced Health Risks:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing obesity-related chronic diseases and improve overall health outcomes.
- Even modest weight loss (e.g., 5-10% of body weight) can lead to meaningful improvements in health parameters, including blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and cholesterol levels.
2. Enhanced Quality of Life:
- Maintaining a healthy weight is associated with improved physical function, mobility, and vitality, leading to a higher quality of life and greater independence.
3. Long-Term Health Promotion:
- Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, promotes long-term health and well-being, reducing the burden of chronic disease and healthcare costs.
Share this article

Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value calculated based on an individual’s height and weight. It is commonly used as an indicator of body fatness and serves as a screening tool for assessing weight status and associated health risks. A BMI of 35 falls within the category of obesity, which is defined as having excess body fat that can negatively impact health. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore BMI, its calculation, significance, health implications, management strategies, and the importance of maintaining a healthy weight.
BMI Calculator
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI):
1. Calculation:
- BMI is calculated using the following formula: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)^2.
- For example, if an individual weighs 100 kilograms and has a height of 1.75 meters, their BMI would be calculated as follows: BMI = 100 / (1.75^2) = 32.65.
2. Interpretation:
- BMI values are categorized as follows:
- Underweight: BMI < 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5 – 24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25 – 29.9
- Obesity:
- Class I (Moderate): BMI 30 – 34.9
- Class II (Severe): BMI 35 – 39.9
- Class III (Very Severe or Morbid): BMI ≥ 40
Health Implications of BMI 35:
1. Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases:
- Obesity, particularly at BMI 35 or higher, is associated with an increased risk of various chronic diseases, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Disease (e.g., heart disease, stroke)
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- Dyslipidemia (Abnormal Cholesterol Levels)
- Certain Cancers (e.g., breast, colorectal)
- Sleep Apnea
- Osteoarthritis
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
2. Impact on Quality of Life:
- Obesity can significantly impair physical function and mobility, leading to decreased quality of life and increased disability.
- Individuals with obesity may experience limitations in activities of daily living and face challenges in social and professional settings.
3. Psychological and Emotional Effects:
- Obesity can have psychological and emotional repercussions, including:
- Low self-esteem
- Depression and anxiety
- Body image dissatisfaction
- Social stigma and discrimination
Management Strategies for BMI 35:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet low in calorie-dense foods and high in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise to promote weight loss, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
- Behavioral Strategies: Implementing behavioral changes such as mindful eating, portion control, and stress management techniques to support long-term weight management.
2. Medical Interventions:
- Pharmacotherapy: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to assist with weight loss. These medications may include appetite suppressants, lipase inhibitors, or medications that alter satiety and energy expenditure.
- Bariatric Surgery: For individuals with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 40 or BMI ≥ 35 with obesity-related comorbidities), bariatric surgery may be recommended as a treatment option. Procedures such as gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding can result in significant and sustained weight loss, along with improvements in obesity-related health conditions.
3. Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Obesity management often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties, including physicians, dietitians, psychologists, and exercise physiologists. Collaborative care allows for comprehensive assessment, individualized treatment planning, and ongoing support for behavior change.
Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
1. Reduced Health Risks:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing obesity-related chronic diseases and improve overall health outcomes.
- Even modest weight loss (e.g., 5-10% of body weight) can lead to meaningful improvements in health parameters, including blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and cholesterol levels.
2. Enhanced Quality of Life:
- Maintaining a healthy weight is associated with improved physical function, mobility, and vitality, leading to a higher quality of life and greater independence.
3. Long-Term Health Promotion:
- Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, promotes long-term health and well-being, reducing the burden of chronic disease and healthcare costs.
